Imagine a world where cars drive themselves, voice assistants answer questions, and social media suggests the perfect content you want to see. This is the world shaped by artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they each have unique roles in bringing smart technology to life. Let’s dive into the basics and see how each of these technologies works—and how they change the way we live and interact with the world around us.
AI, Machine Learning, And Deep Learning: Breaking It Down
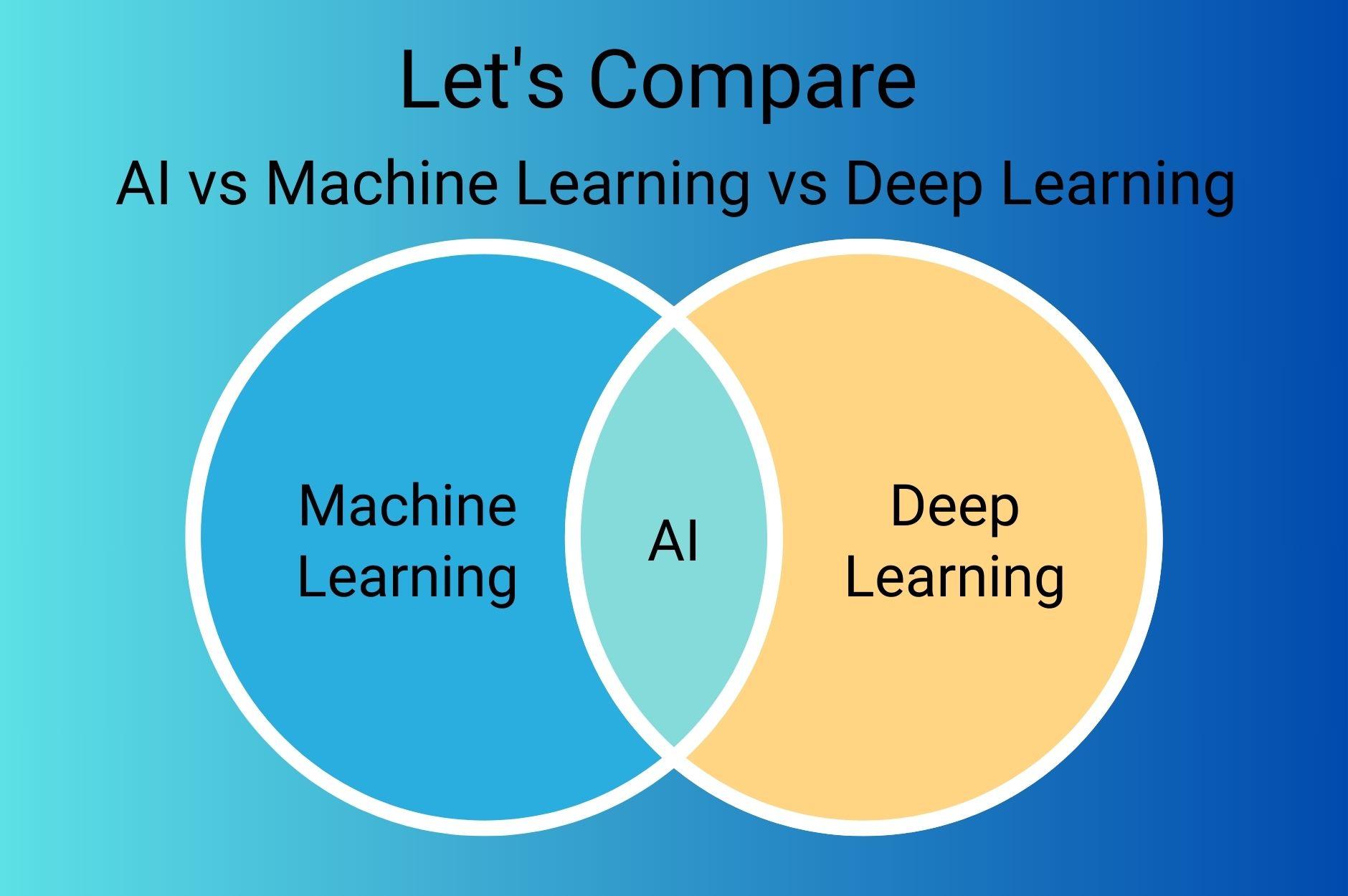
Let’s begin by understanding where each of these technologies sits in the big picture:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the broadest category.
- Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of AI.
- Deep Learning (DL) is a specialized subset of machine learning.
Each level becomes more specific, focusing on ways to make machines “think” and act intelligently. Let’s explore each concept in more detail.
What Is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial Intelligence, or AI, is the broad field focused on creating machines that can simulate human intelligence. This means that AI can be any computer program or system that performs tasks typically requiring human thought, like understanding language, recognizing patterns, making decisions, or solving problems.

Key Aspects Of AI:
- Automation of tasks: AI is designed to automate repetitive or complex tasks. For instance, email filters or smart assistants like Siri are forms of AI that help make everyday tasks easier.
- Wide range of capabilities: AI doesn’t just include one approach or technology. It encompasses everything from simple algorithms to advanced robots and intelligent chatbots.
Example:
Consider smart home systems that adjust lights or thermostats based on your preferences. They use AI to learn from your behavior and make adjustments that match your daily routine.
Types Of AI:
AI can be broken down into three main types:
- Narrow AI: AI specialized in a single task, like playing chess or recognizing faces.
- General AI: A more advanced AI capable of thinking and reasoning across various tasks (this doesn’t exist yet but remains a goal).
- Super AI: Hypothetical AI that surpasses human intelligence (currently in the realm of science fiction).
What Is Machine Learning (ML)?
Machine Learning is a branch of AI, but it’s more focused. ML enables computers to learn from data without explicit programming for each task. Think of machine learning as giving computers the ability to “practice” on data and improve over time.

How Machine Learning Works:
In ML, data is fed into algorithms to help a machine “learn” patterns. As it processes more data, it gets better at tasks, like identifying images or making predictions.
Key Aspects Of Machine Learning:
- Data-driven: Machine learning relies on vast amounts of data. For example, to teach a machine to recognize cats, you’d show it thousands of cat pictures.
- Improvement over time: ML models get better as they see more examples. This is why machine learning-powered apps like Google Photos can recognize people in your pictures with increasing accuracy.
Types Of Machine Learning:
- Supervised Learning: The algorithm is trained on labeled data, like identifying spam emails by showing it both spam and non-spam examples.
- Unsupervised Learning: The algorithm finds patterns in unlabeled data. For example, it might group customers based on buying habits.
- Reinforcement Learning: The algorithm learns through a trial-and-error approach, receiving rewards or penalties based on its actions, like training a robot to navigate a maze.
What Is Deep Learning (DL)?
Deep Learning is a specialized subfield of machine learning. It’s based on neural networks, which are inspired by the human brain. Deep learning algorithms are designed to automatically process large amounts of unstructured data—like images, videos, and texts.

How Deep Learning Works:
Deep learning algorithms use layers of “neurons” that mimic the way the human brain processes information. These neural networks can recognize complex patterns in data, making them ideal for tasks like image and speech recognition.
Key Aspects Of Deep Learning:
- Neural Networks: Deep learning models use neural networks with multiple layers, called “deep” because of their complex structure.
- Big Data and Processing Power: Deep learning requires significant computing power and a lot of data to train, which is why it only recently became popular as technology advanced.
Example:
Consider facial recognition. Deep learning models can scan a face, recognize features like eyes and nose, and compare them with known faces to identify a person. It’s why platforms like Facebook can suggest tags in photos.
Applications Of Deep Learning:
Deep learning is particularly useful in applications that involve:
- Image recognition: Analyzing medical images for diagnosis.
- Speech recognition: Transcribing spoken words into text.
- Natural language processing: Powering chatbots and translation services.
AI, Machine Learning, And Deep Learning In Everyday Life
To see these technologies in action, let’s look at some familiar examples.
- Self-Driving Cars: These vehicles rely on AI for overall operation, machine learning to recognize road signs and predict other drivers’ actions, and deep learning to detect and process images from cameras.
- Personalized Recommendations: Streaming platforms use machine learning to recommend shows based on your watching history, while deep learning can analyze broader viewing trends.
- Voice Assistants: Siri and Alexa use AI to understand and respond to commands, while deep learning algorithms help them understand natural language.
Key Differences Summarized
Let’s put the differences between AI, ML, and DL into perspective:
| Aspect | Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Machine Learning (ML) | Deep Learning (DL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scope | Broad | Subset of AI | Subset of ML |
| Goal | Mimic human intelligence | Learn from data | Learn from data through neural networks |
| Data Needs | Varies | High | Very High |
| Computing Power | Varies | Moderate | High |
| Examples | Smart assistants, automated cars | Spam filtering, recommendation systems | Facial recognition, voice recognition |
Why These Differences Matter
Understanding these differences isn’t just about technical details—it’s about seeing how different levels of intelligence shape technology’s role in our lives. AI brings a layer of intelligence to basic tasks, ML allows systems to personalize experiences, and DL pushes boundaries by recognizing complex patterns that mimic human perception.
As AI, ML, and DL continue to evolve, they’ll open doors to innovations in fields like healthcare, finance, entertainment, and beyond. Knowing what each technology does and where it fits in helps us appreciate both the possibilities and challenges these advancements bring.
Final Thoughts
In a world where technology constantly changes, knowing the basics of AI, machine learning, and deep learning can help us stay informed and ready for what’s next. While each technology has unique strengths, they’re all part of a shared goal—making machines smarter and more capable. The more we understand these tools, the better we can harness them to improve our daily lives, solve problems, and create a future filled with exciting possibilities.
So, whether it’s in the smartphone apps we use daily or in the cars of tomorrow, AI, machine learning, and deep learning are shaping a new era of intelligence. And now, you know how each piece fits into the bigger picture!

One thought on “AI vs. Machine Learning vs. Deep Learning: Key Differences”